Orbital Fracture
What is an orbital fracture?
An orbital fracture is a break in one or more of the seven bones that surround the eye. These bones form a “box” that protects the eye. The bottom (orbital floor) and the inside wall (near the nose) are the thinnest and easiest to break.
When something hits the eye, the force goes into the eye socket (called the orbit). The thin bones can bend or break from this pressure. This break is called an orbital fracture. Sometimes, this release of force can actually protect the eye from a more serious injury.
Children can get a special kind of orbital fracture called a trapdoor fracture (or “white-eye fracture”). In this injury, a piece of bone bends open, soft tissue like muscle slips through, and then the bone flap closes again. The trapped tissue loses blood supply and keeps the eye from moving normally. This often causes nausea and vomiting.
Figure 1: Bones of the orbit form the roof, inner wall, outer wall, and floor.
After a fracture, muscles, fat, or connective tissue around the eye may be bruised or pushed out of place. If too much tissue is lost, the eye may sink back into the socket (enophthalmos), which can affect both appearance and vision. If muscles are injured, eye movements may be limited and double vision may occur.
What causes an orbital fracture?
Orbital fractures can happen from:
- Falls
- Sports injuries (such as being hit by a fast ball)
- Violence (punches, elbows)
- Car accidents
These injuries are more common in boys than in girls. Wearing protective sports glasses can help lower the risk.
What are the symptoms of an orbital fracture?
Common symptoms include:
- Bruising, swelling, and pain around the eye
- Redness in the eye
- Double vision (seeing two images at the same time)
- Numbness in the cheek, nose, or teeth
Signs of a fracture can include:
- A change in the smooth curve of the bone around the eye
- Trouble moving the eye (especially up and down)
- Air under the skin around the eye
Trapdoor fractures may cause:
- Pain when moving the eye
- Nausea or vomiting
- Double vision
Even when redness is mild, these symptoms may point to a trapdoor fracture. In all cases, an eye exam by an ophthalmologist is very important.
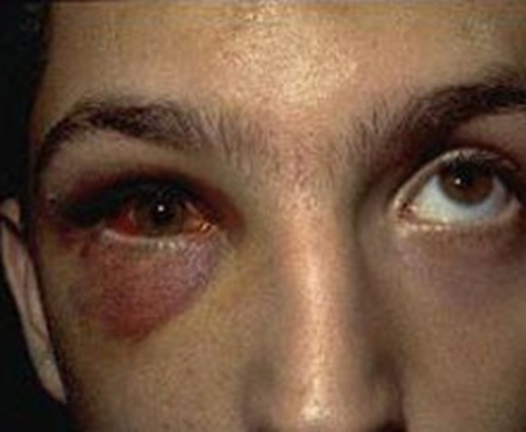
Figure 2: Bruising around the eye is a common symptom. The right eye cannot move upward like the left eye.
What causes an orbital fracture?
A CT scan of the eye socket is the best way to confirm an orbital fracture. Sometimes, if radiation is a concern, an MRI may be used instead.
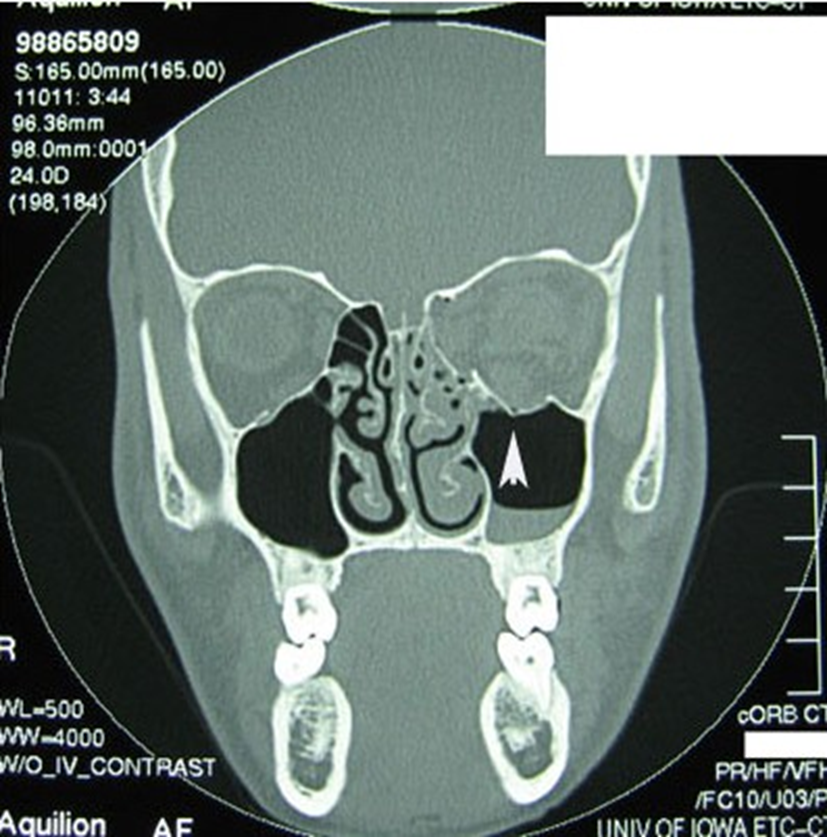
Figure 3: CT scan showing a fracture with the arrow head.
Are there different types of orbital fractures?
Orbital fractures can vary by:
- Size (small or large)
- Location (front or back of the socket)
- Whether the bone is displaced (moved out of place)
- Whether tissue or muscle is trapped (trapdoor fracture)
- Symptoms (like double vision, pain, or eye sinking)
A simple fracture causes little or no double vision and does not make the eye sink back once healing occurs.
What can be done for a simple orbital fracture?
Most simple orbital fractures heal without surgery. Treatment may include:
- Ice to reduce swelling
- Decongestants to help drain blood and fluid from sinuses
- Avoiding nose-blowing (prevents sinus contents from moving into the orbit)
- Oral steroids in some cases (to reduce swelling and scarring)
- Oral antibiotics (may be needed if a sinus inflammation is present)
When should surgical repair of orbital fractures be considered?
Trapdoor fractures usually need surgery within 24–48 hours to free trapped tissue.
For other fractures, doctors may wait and watch. Double vision often improves on its own over a few weeks. Surgery may be needed if:
- Double vision does not improve
- The eye sinks into the socket (enophthalmos)
Surgery usually takes place within a few weeks to months, depending on the case. Surgical repair may include:
- Exploring the fracture site and repositioning bone
- Releasing trapped tissue
- Covering the fracture with synthetic material
What can be done for a simple orbital fracture?
Most fractures heal without lasting problems. In some cases, though:
- Strabismus surgery (eye muscle surgery) may be needed for ongoing double vision
- Eye socket surgery may be needed to fix a sunken appearance of the eye
- Persistent double vision may also be treated with special glasses (prisms) or botulinum toxin injections
Swelling of the eye muscles seen on CT scans can sometimes help predict if double vision will continue.
What can be done for a simple orbital fracture?
An orbital fracture is a break in the thin bones around the eye, often caused by trauma. Symptoms may include swelling, bruising, double vision, or numbness in the face. Children may develop a special type called a trapdoor fracture, which can be serious and often needs urgent surgery. Most simple fractures heal without surgery and can be managed with ice, medicine, and rest. Some patients may later need surgery if vision problems or changes in eye position do not improve. Regular follow-up with an eye doctor is important to protect both vision and appearance.